Causes of heating of automotive relays
1. How to detect the quality of automotive relays:
a. Open circuit detection
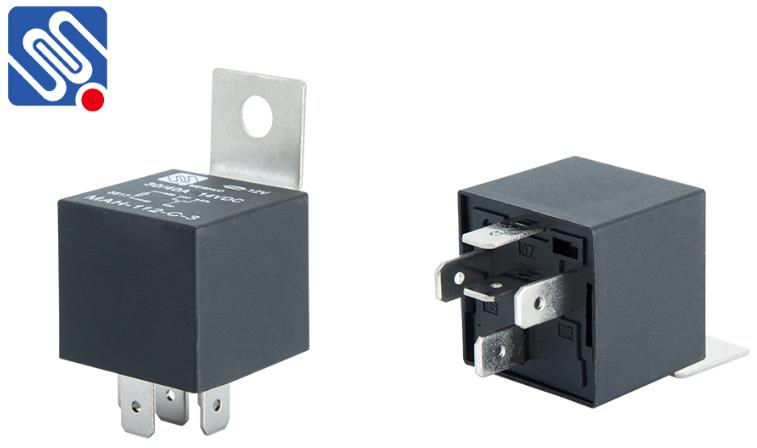
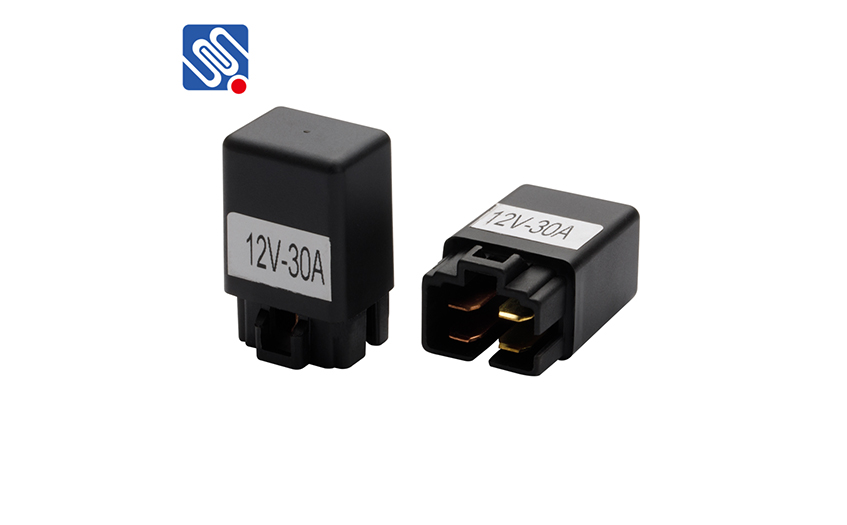
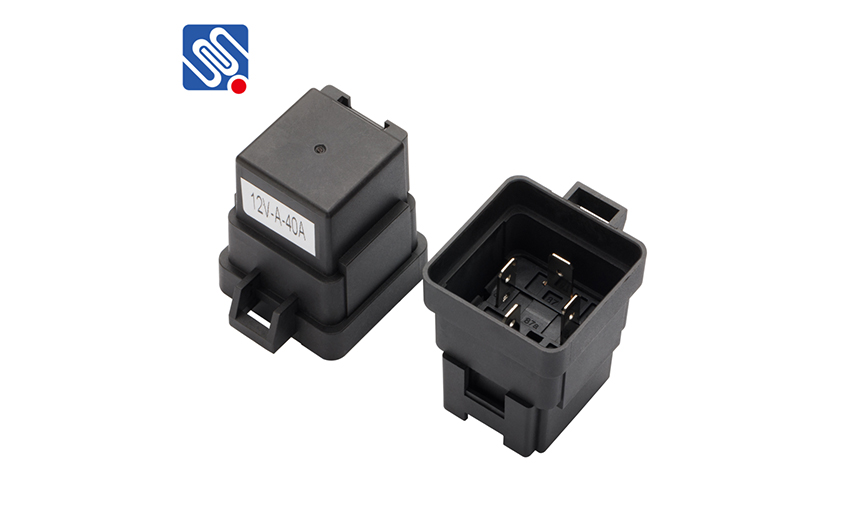
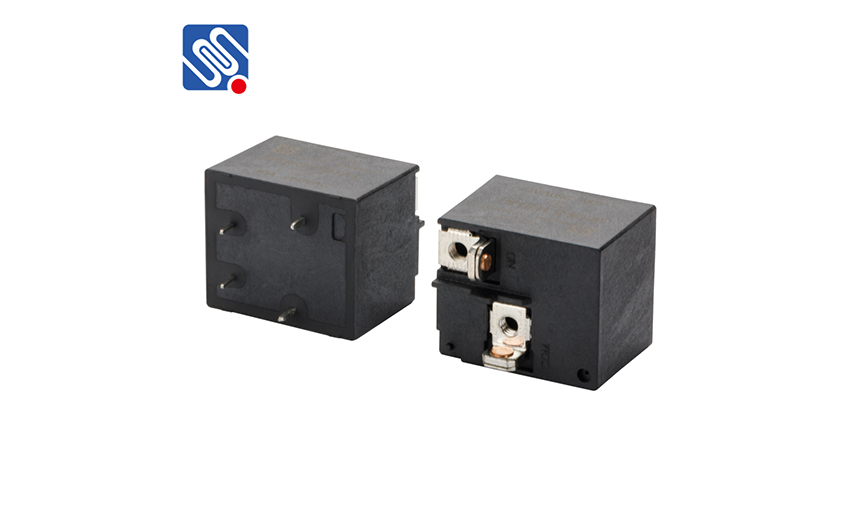
The resistance measurement method with a multimeter can be used to check the quality of the relay. Use a multimeter to check that the pins (85) and (86), (87) and (87a) should be connected. The resistance between (87) and (30) should be ∞. If the check result is not consistent with the above rules, it indicates that there is a problem with the relay.
b. Power-on detection
If there is no problem in the above inspection, you can add 12V power supply between (85) and (86) pins, and use a multimeter to check that (87) and (30) should be connected. If the above rules are not met, or the relay heats up after power-on, it means that it has been damaged.
2. The phenomenon and reason of relay heating:
a. Abnormal heating occurs in the center of the contact, and the contact is fused, melted, dissolved and solidified, etc., and the operation is not good. That is because the repeated switching of the contacts causes the continuous occurrence of opening and closing arcs;
b. The internal circuit of the relay is fused and the contact is melted and solidified, and the operation is not good. This is probably due to abnormal overcurrent exceeding the rated current of the contact;
c. The coil is partially short-circuited and fused, the coil is disconnected, and the coil remains abnormally heated. It may be an overvoltage applied to the coil;
The solutions to the above phenomena are:
a. For AC specification relays, the voltage should not be less than 90% of the rated voltage; for DC specification relays, the voltage should not be less than 79% of the rated voltage; avoid high-frequency switching;
b. Carry out safety design on the circuit to prevent the rated current exceeding the contact from flowing through the contact circuit;
c. Do not apply a voltage above the rated voltage to the coil.








 selena
selena  sales@msrelay.com
sales@msrelay.com 13968707033
13968707033
 +86-577-62518811
+86-577-62518811





