relay comparison: understanding the key differences between relay types and their applications
Release time:2025-12-06 23:34:34
In electrical engineering, relays are crucial components that act as switches, controlled by electrical signals. They serve as intermediaries between low-power circuits and high-power devices, protecting systems from overloads, controlling circuits, and facilitating automation. A relay comparison involves analyzing different types of relays based on their characteristics, performance, applications, and suitability for specific environments. This article provides an overview of various relay types, such as electromagnetic, solid-state, and thermal relays, comparing their functionalities and typical use cases.
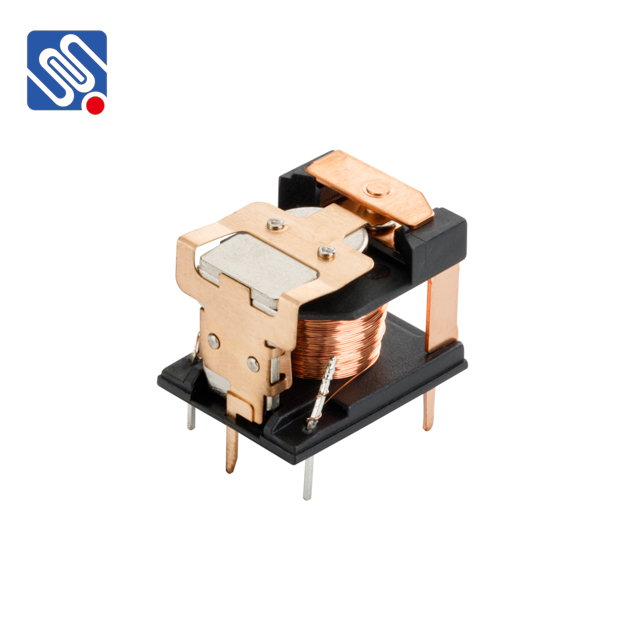
1. Types of Relays
The first step in a relay comparison is understanding the various types of relays, each designed for specific functions in electrical systems. The most common types include:
Electromagnetic Relays (EMR): These are the traditional type of relays, consisting of a coil of wire that, when energized, generates a magnetic field to operate mechanical contacts. They are widely used in low- to medium-power applications, offering simple operation and cost-effectiveness.
Solid-State Relays (SSR): Unlike EMRs, solid-state relays rely on semiconductor components to switch the circuit. SSRs are known for their durability and faster switching speeds, as they have no moving parts. They are often used in high-frequency or high-reliability applications.

